Pneumonia vs Tuberculosis: Key Differences, Symptoms & Treatment
Both Pneumonia and Tuberculosis are lung diseases that can cause cough, fever, and breathing difficulty. When symptoms overlap, many people search for answers and begin comparing Pneumonia vs Tuberculosis to understand what might be affecting their health.
For someone struggling with persistent cough, chest discomfort, or fatigue, it can be difficult to tell the difference between the two. While the symptoms may seem similar at first, the cause, severity, treatment, and recovery process for each condition are very different.
Knowing how these illnesses differ can help you recognize early warning signs and seek the right medical care at the right time.
What is Pneumonia?
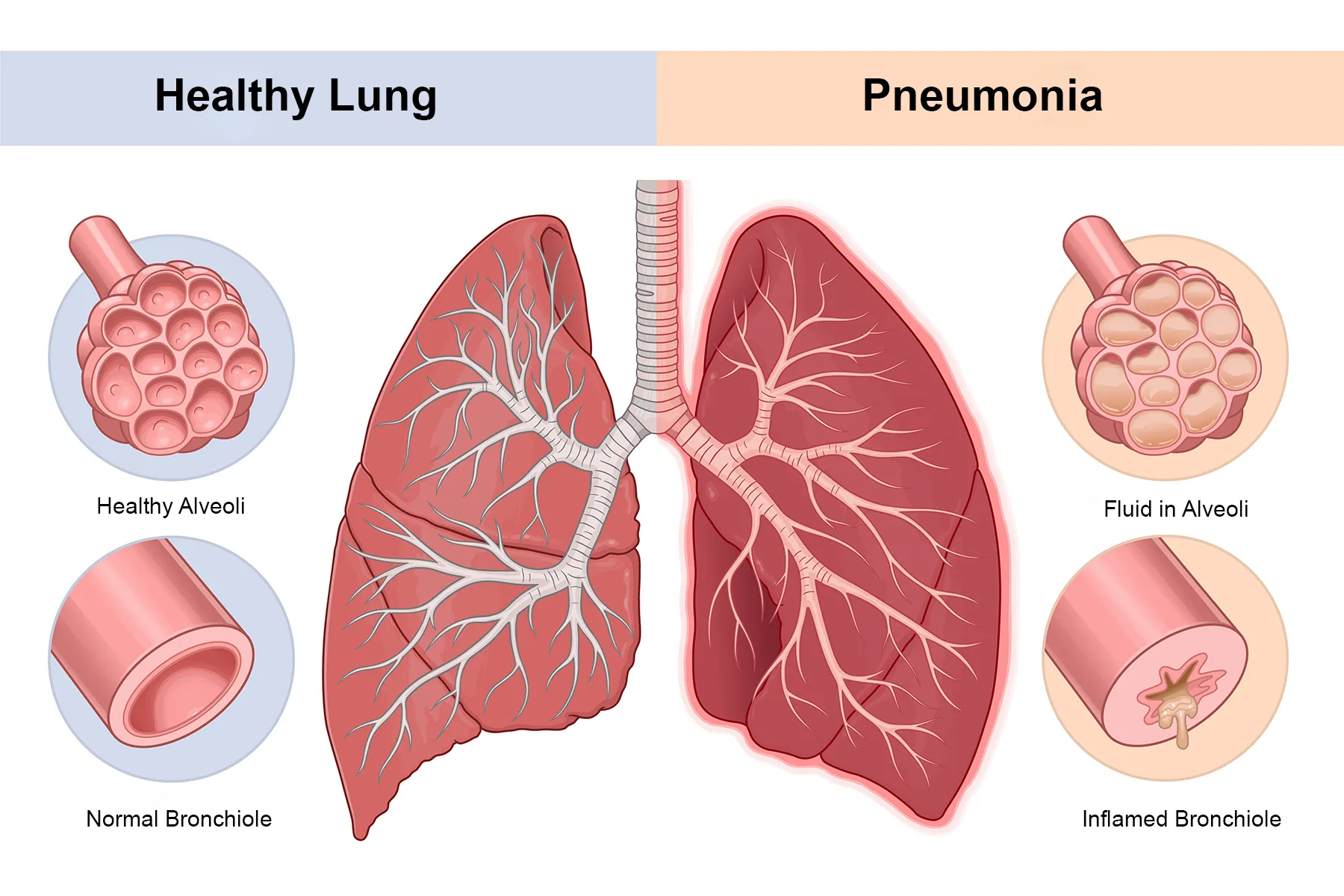
Pneumonia is an infection of the lungs where the air sacs (alveoli) become inflamed and may fill with fluid or pus. This leads to breathing difficulty and reduced oxygen supply to the body.
Cause and Transmission
Pneumonia can be caused by:
Bacteria (most common)
Viruses (such as influenza)
Fungi (less common)
It can spread through:
Coughing and sneezing
Touching contaminated surfaces and then touching your face
Inhaling microorganisms in the air
It usually affects people who have:
- Low immunity
Chronic respiratory conditions
Smoking habits
Symptoms of Pneumonia
High fever and chills
Persistent cough (often with yellow or green mucus)
Shortness of breath
Chest pain during breathing or coughing
Fatigue and weakness
If the illness is severe, breathing can become difficult, requiring urgent medical care.
Diagnosis
Chest X-ray to see infection in the lungs
Blood tests to detect infection
Sputum tests to identify the organism
Pulse oximetry to check oxygen levels
Treatment
Antibiotics for bacterial pneumonia
Antiviral medication for viral infections
Cough and fever relief medications
Fluid intake and rest
Severe cases may require:
Hospital care
Oxygen support
Complications of Pneumonia
Respiratory failure
Fluid accumulation around lungs
Sepsis (serious infection in the blood)
Prevention
Get vaccinated (especially for children, seniors, and high-risk individuals)
Wash hands regularly
Avoid smoking
Strengthen immunity with balanced nutrition

What is Tuberculosis (TB)?
Tuberculosis is a chronic bacterial infection caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis. It primarily affects the lungs but can spread to the bones, kidneys, brain, or lymph nodes if not treated.
Cause and Transmission
TB spreads through the air when a person with active TB coughs, sneezes, or speaks.
Unlike pneumonia, TB symptoms develop slowly and last for weeks or months.
TB does not spread by:
Sharing food or utensils
Touching clothes or shaking hands
Symptoms of Tuberculosis
Persistent cough for more than 2–3 weeks
Evening or night fever
Weight loss and loss of appetite
Night sweats
Chest pain
Coughing blood (in advanced cases)
Diagnosis
Treatment
TB treatment requires:
Multiple medications taken together
Duration of 6 months or longer
Stopping treatment early can cause:
TB relapse
Drug-resistant TB (much harder to treat)
Regular follow-up is essential during treatment.
Complications of Tuberculosis
If left untreated, TB may:
Damage lung tissue
Spread to other organs
Cause long-term breathing issues
Become life-threatening
Prevention
BCG vaccine in childhood
Proper ventilation in indoor spaces
Wearing a mask when coughing
Early diagnosis and complete treatment
Key Differences: Pneumonia vs Tuberculosis
| Feature | Pneumonia | Tuberculosis |
|---|---|---|
| Speed of Onset | Sudden, rapid | Slow, gradual |
| Main Cause | Bacteria/virus/fungus | Mycobacterium tuberculosis |
| Contagiousness | Moderate | Highly contagious (airborne) |
| Treatment Duration | 1–2 weeks | 6+ months |
| Common Symptom Pattern | High fever, wet cough | Persistent cough, weight loss, night sweats |
Conclusion
Understanding the difference between Pneumonia vs Tuberculosis can help you recognize early warning signs and seek timely medical care. While pneumonia usually appears suddenly and responds quickly to treatment, tuberculosis develops slowly and requires long-term medication and consistent follow-up.
If you or a loved one has a cough lasting more than two weeks, unexplained fever, chest discomfort, or difficulty breathing, it is important to consult a Pulmonologist for proper evaluation. Early diagnosis not only improves recovery but also prevents complications and protects others around you.
For more guidance on lung health and respiratory care, continue learning and stay informed – your health is within your control.
MBBS, DNB, IDCCM.,
Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine
Shifa Hospitals
