Bypass Surgery vs Open Heart Surgery: Differences, Risks and Recovery
Heart-related problems can be frightening, especially when a doctor mentions surgery. At that moment, many patients and their families hear two common terms open heart surgery and bypass surgery and immediately feel confused. Are these two surgeries the same? Is one more serious than the other? Which one is safer?
This confusion is very common. Because of medical terms and fear, people often assume the worst. However, when explained in simple language, the difference between bypass surgery vs open heart surgery becomes easy to understand. Both surgeries are performed to save lives and improve heart health. They are recommended only when other treatments are not enough.
Heart disease is a serious issue, but modern medicine has made heart surgeries much safer and more successful than before. Understanding why a surgery is needed, how it is done, and what life looks like after surgery helps patients and their relatives feel more confident and prepared.
What Is Open Heart Surgery?
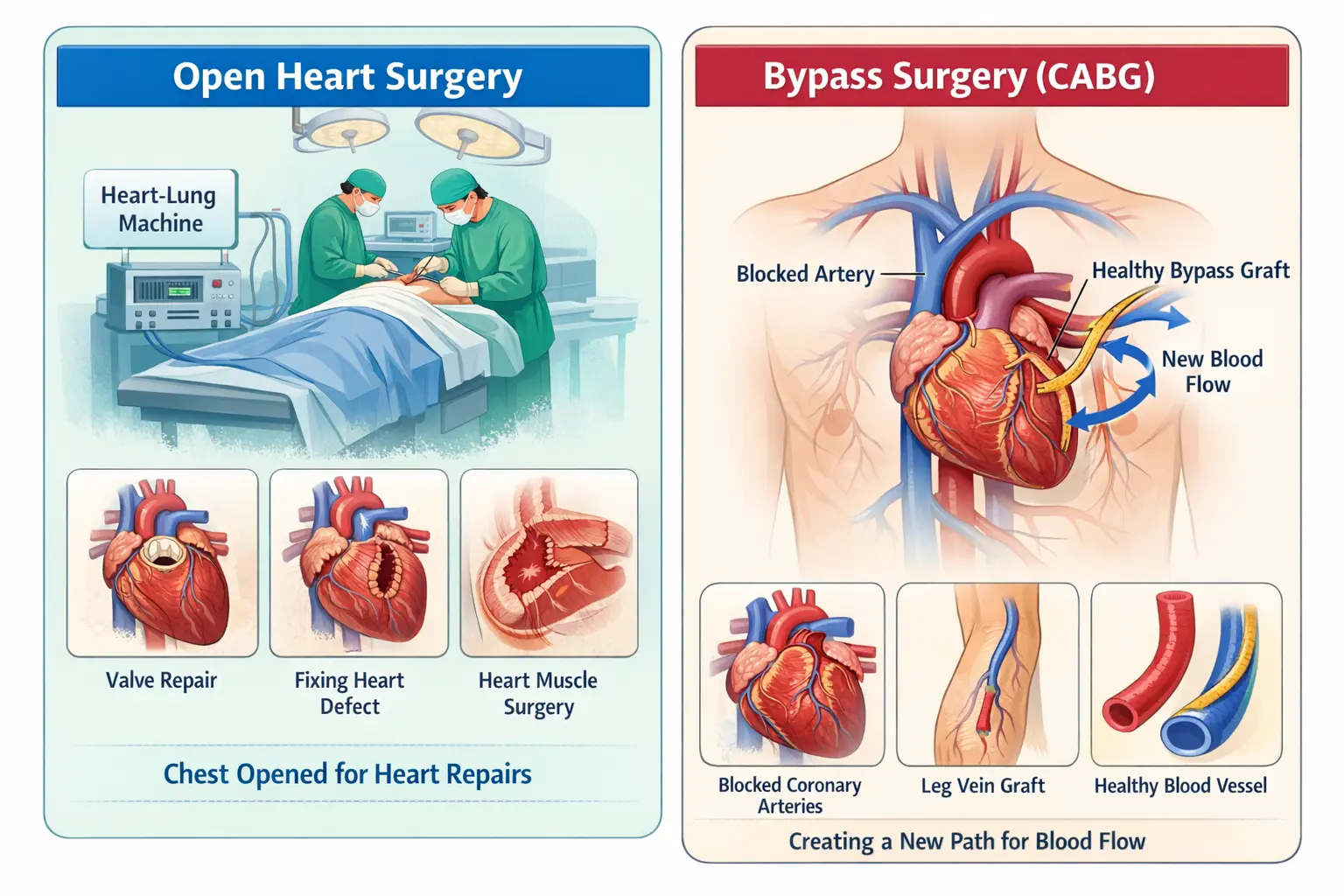
Open heart surgery is not one single operation. Instead, it is a category of heart surgeries. In this type of surgery, the chest is opened so that doctors can directly see and operate on the heart.
In most cases, the heart is temporarily stopped during the procedure. A heart lung machine is used to keep blood flowing throughout the body. This allows surgeons to work on the heart safely and accurately.
Open heart surgery has been performed for many decades. Over time, it has become safer due to better technology, improved surgical skills, and advanced post-surgery care.
Open Heart Surgery Procedure
The procedure usually follows these steps:
The patient is given anesthesia and put to sleep
The chest bone is carefully opened
The heart is accessed safely
The required repair or correction is done
The heart is restarted, and the chest is closed
Although this may sound scary, it is a well-planned and controlled process performed by experienced medical teams.
Conditions That Require Open Heart Surgery
Open heart surgery is advised when problems inside the heart cannot be treated with medicines or minor procedures.
Common conditions include:
Damaged or narrowed heart valves
Holes between heart chambers (congenital defects)
Heart muscle diseases
Severe infections affecting heart valves
In these situations, bypass surgery alone will not solve the problem. Therefore, a specific type of open heart surgery is required.
Risks & Complications of Open Heart Surgery
Like any major surgery, open heart surgery has some risks. However, serious complications are uncommon when surgery is done at the right time.
Possible risks include:
Infection
Bleeding
Temporary weakness or tiredness
Longer recovery period
Doctors carefully assess each patient before surgery to reduce these risks as much as possible.
What Is Bypass Surgery?
Bypass surgery, also called Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting (CABG), is performed when the blood vessels supplying the heart become blocked.
These blockages are usually caused by cholesterol and fat buildup. When blood flow to the heart muscle is reduced, symptoms like chest pain, breathlessness, or heart attacks can occur.
In bypass surgery, a new pathway is created for blood to flow. This allows oxygen-rich blood to reach the heart muscle properly again.
Bypass Surgery Procedure
The procedure usually includes:
Identifying blocked heart arteries
Taking a healthy blood vessel from the chest, leg, or arm
Attaching this vessel above and below the blockage
Allowing blood to bypass the blocked area
Since the chest is opened during this process, bypass surgery is a type of open heart surgery.
Conditions That Require Bypass Surgery
Bypass surgery is recommended when blockages are severe or widespread.
Doctors may advise bypass surgery when:
Multiple heart arteries are blocked
Blockages are very severe
Stents are not suitable or have failed
Diabetes is present with heart disease
The main heart artery is blocked
In such cases, bypass surgery offers better long-term results.
Risks & Complications of Bypass Surgery
Most patients recover well after bypass surgery. Still, some temporary issues may occur.
Possible complications include:
Infection at the surgical site
Chest pain during healing
Temporary memory or concentration issues
Irregular heartbeat
These issues are usually manageable with proper medical care and follow-up.
Bypass Surgery vs Open Heart Surgery: Key Differences
This is the most important section to understand the confusion clearly.
| Aspect | Open Heart Surgery | Bypass Surgery |
|---|---|---|
| Meaning | A category of surgeries | A specific surgery |
| Purpose | Fixes heart structure | Treats blocked arteries |
| Chest opened | Yes | Yes |
| Heart stopped | Often | Often |
| Examples | Valve repair, defect correction | CABG |
| Goal | Correct heart problems | Improve blood flow |
In short, bypass surgery is a type of open heart surgery, but not all open heart surgeries are bypass surgeries.
How Serious Are These Surgeries?
Both surgeries are major procedures, but they are also routine and well-practiced today. With modern equipment and trained specialists, success rates are high.
The seriousness depends on:
Age of the patient
Overall health
Presence of diabetes or kidney disease
Heart function before surgery
Doctors recommend surgery only when the benefits clearly outweigh the risks.
Survival Rate & Life Expectancy After Bypass Surgery
Bypass surgery is known to improve quality of life and life expectancy. Many patients live long, active lives after recovery.
Benefits include:
Reduced chest pain
Lower risk of heart attack
Better heart function
Improved daily activity levels
However, long-term success depends on lifestyle changes and regular medical follow-ups.
Life After Surgery: What Patients Can Expect
After recovery, most patients return to normal activities.
Common improvements include:
Better breathing
Increased energy
Improved sleep
Less chest discomfort
Although recovery takes time, patience and proper care make the journey smoother.
How to Take Care of Patients After Surgery
Post-surgery care is very important for good recovery.
Key care tips:
Keep the wound clean and dry
Follow the doctor’s medication plan
Encourage gentle walking
Provide emotional support
Attend follow-up appointments
Family support plays a big role in faster healing.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Is bypass surgery painful?
Pain is managed well with medicines. Most discomfort reduces within weeks.
Can bypass surgery be avoided?
In early stages, lifestyle changes and medicines may help. Severe cases need surgery.
How long does recovery take?
Initial recovery takes 6–8 weeks, while full recovery may take a few months.
Is bypass surgery safe for elderly patients?
Yes, when properly evaluated, it can be safely performed even in older patients.
Conclusion
Understanding the difference between bypass surgery vs open heart surgery helps reduce fear and confusion. Open heart surgery is a broad term that includes many procedures, while bypass surgery is specifically done to treat blocked heart arteries. Both surgeries are proven, safe, and life-saving when recommended at the right time.
Heart problems are serious, but they are also treatable. With the right information, proper medical care, and family support, patients can recover well and lead a healthy life. Learning more and asking the right questions always helps in making confident and informed decisions about heart health.
M.B.B.S., M.D.(General Medicine) D.M.(Cardiology)., FNB
Cardiology
Shifa Hospitals
